指针是一个存储其他变量地址的变量。
考虑以下语句 -
'int qty = 179;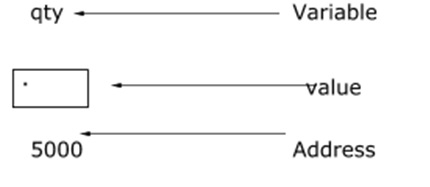
声明指针 h2>
声明指针的语法如下 -
'int *p;这里,'p'是一个指针变量,它保存其他变量的地址。
指针的初始化
地址运算符(&)用于初始化指针变量.
例如,
'int qty = 175;
int *p;
p= &qty;指针数组
它是地址集合(或)指针集合。
声明
以下是指针数组的声明 -
'datatype *pointername [size];例如,
'int *p[5];It represents an array of pointers that can hold five integer element addresses.
Initialization
‘&’ is used for initialization
例如,
'int a[3] = {10,20,30};
int *p[3], i;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) (or) for (i=0; i<3,i++)
p[i] = &a[i];
p[i] = a+i;Accessing
Indirection operator (*) is used for accessing.
例如,
'for (i=0, i<3; i++)
printf ("%d", *p[i]);程序
以下是使用指针计算数组元素之和的 C 程序 -
现场演示
'//sum of array elements using pointers
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
void main(){
int i, n, sum = 0;
int *ptr;
printf("Enter size of array : <p>");
scanf("%d", &n);
ptr = (int *) malloc(n * sizeof(int));
printf("Enter elements in the List </p><p>");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d", ptr + i);
}
//calculate sum of elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
sum = sum + *(ptr + i);
}
printf("Sum of all elements in an array is = %d</p><p>", sum);
return 0;
}</p>输出
当执行上述程序时,会产生以下结果 -
'Enter size of array:
5
Enter elements in the List
12
13
14
15
16
Sum of all elements in an array is = 70


